How IP and MAC address work?
Using the internet and connecting various devices with it you might have come across the concept of IP and MAC addresses. Many people confuse them with being the same but in reality, these are a lot different than each other. IP addresses are the internet addresses depicting the very address using which a computer is connected with the internet. Whereas MAC address is known as media access control and it is the physical address of the device connected with the internet.
Any web browser that is browsing the internet uses a designated IP address for the sake of transmitting the data that a user has requested from the browser. The address is inserted into the data packets that the network software stack sends out. The data packets are recognized by the device and acknowledged by the IP address and then the DNS transfers these data packets into a viable set of information and the systems do the rest, transmitting results to your screen.
Harmony of IP address and MAC address
Local network translates the IP address to a MAC address and adds the MAC address to the data stream which then sends the data to the right device. In reality, both the MAC and IP addresses work in absolute harmony to transfer the data back and forth and then interchanging information with one and the other. But still, both of these are completely different.
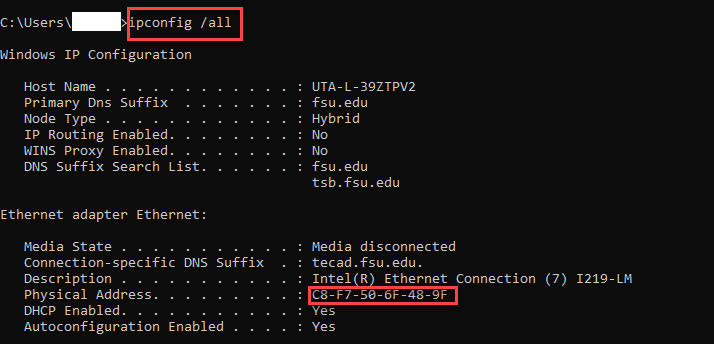
What is a MAC address?
MAC address refers to a piece of hardware that will control how the data would be pushed out onto a network. MAC is a layer 2 device and MAC address is a layer 2 address in the OSI reference model. In the modern era where it is quite common to have established a dedicated network connection, many devices are connected with the help of LAN or are connected with the help of the Wi-Fi system. Both these methods use the MAC addresses in order to identify that device on the network.
Start Your 7-Day FREE TRIAL with QuickStart
The MAC address consists of a total of 12 hexadecimal digits that are paired in the form of a group and uses hyphens to separate each other. The first half of a MAC address refers to the manufacturer ID while the second half is used as the device identifier. This number is hardcoded within the device following its manufacturing process. The overall approach of the MAC addresses strives to make sure that the possibility of two devices jumping up in a network connection with the same physical addresses will become highly unlikely.
Not two same devices should have the same MAC address when combing up on a network connection, if that does ever happen then these devices would be running into communication-related problems and the network would become seriously confused about which device should receive the packet.
What is an IP address?
The IP address does control how the devices on the internet would communicate with each other and also defines the behavior of the internet routers at the same time. In the OSI reference model, it is considered to be a layer 3. The internet was initially developed around the IP version 4 IPv4 and is now slowly being transitioned to IPv6.
An IP address identifies a device onto the global network. An IPv4 address would consist of 32 bits that were usually written as the four decimal numbers. The possible set of values ranges from 000.000.000.000 to 255.255.255.255 although many specific IP addresses in between are not allowed or specifically restricted to be used for other specific purposes.
The IP address combines the network and device identification data. The network prefix is anywhere from eight to the 31 bits and the work of the remainder is to identify the device onto the network. The number of internet-connected devices is increasing day by day which has caused serious havoc and workload for the IPv4 and thus the reason why it is being shifted to or updated as IPv6.
Another major difference between a MAC and IP address is their availability to change. An IP address is bound to a network device and using different software or tool based configurations it can be changed at any possible time. MAC addresses however can't be changed no matter the circumstances because these are deeply embedded into the machine. That is where the concept of ARP comes into play, it is the address resolution protocol that maps the IP addresses to the MAC addresses. When a data packet is sent to the switch by the internet, it used the ARP mechanism for the sake of identifying which specific MAC address the packet should be sent to.
This is the mechanism right here which stops the whole internet from spiraling out and keeps a sense of harmony going on through and through. If you are interested in becoming a professional IT expert then CompTIA certification training can help you achieve it without any problem.
